Universal Guide to Managed File Transfer (MFT) Software
What is MFT? This guide offers everything you need to know about using managed file transfer to securely move data inside and outside of your enterprise.

MFT, or managed file transfer, is used by just about every enterprise. After all, data is the lifeblood of modern business. It’s also your most valuable asset, the future, and whatever other metaphor you want to use. Somehow, data is both everything and everywhere. Paradoxically, it’s here and needs to get over there. And if you’re reading this article, it’s probably your job to make that move happen.
So, how do large enterprises currently share files? You guessed it, they use secure MFT software. In this Universal Guide to Managed File Transfer, we’ll dive into what MFT means, what it does, and what’s coming next.
What is MFT?
MFT stands for managed file transfer, a type of software that enables the exchange of electronic data between systems, people, and organizations in a secure, reliable manner.
Compared to ad-hoc approaches, modern managed file transfer software platforms offer advanced capabilities, security, and control while also enabling multiple file transfer protocols.
For a more comprehensive MFT definition, read the blog post, What is Managed File Transfer?
Important Managed File Transfer Concepts to Understand
Ad-hoc File Transfers
An ad-hoc file transfer is when information is manually shared between users or organizations. They’re unplanned and often unpredictable, yet they frequently occur throughout every organization. After all, any email with an attachment is an ad-hoc file transfer, as are links to files saved to cloud-based storage.
DMZ
A DMZ serves as a buffer between an organization’s protected, trusted internal network and the rest of the internet. It’s named after demilitarized zones that serve as the neutral territory between warring factions.
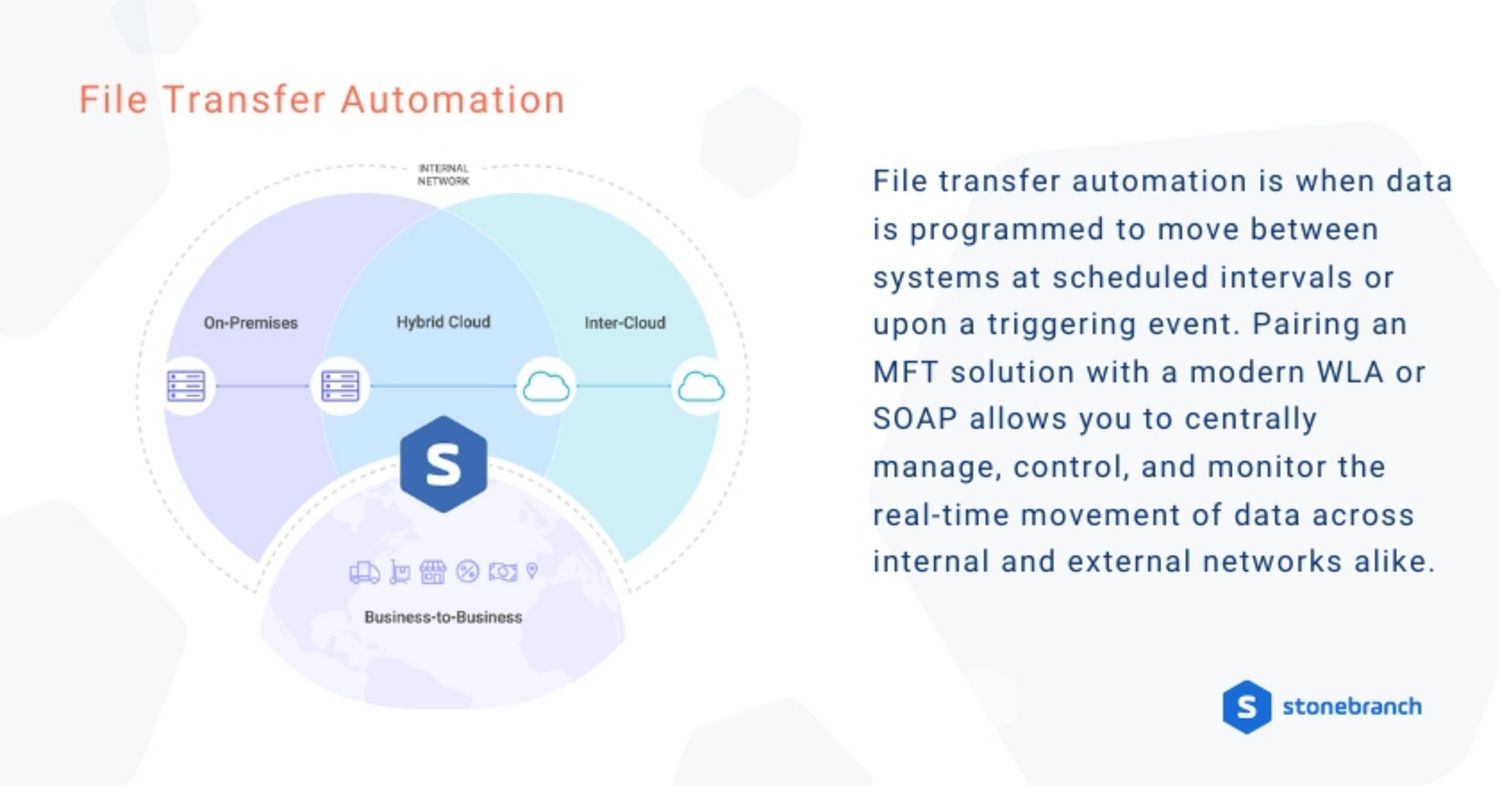
File Transfer Automation
File transfer automation is when data is programmed to move between systems at scheduled intervals or upon a triggering event. Modern workload automation (WLA) and service orchestration and automation platforms (SOAPs) typically offer native MFT solutions. This pairing makes it possible to centrally manage, control, and monitor the real-time movement of data throughout your organization.
FIPS
In the United States, federal information processing standards (FIPS) are set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) following the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and approved by the Secretary of Commerce. These standards, recommendations, and requirements set the benchmark for securing federal computing systems and data. Many private sector organizations follow them as well. There are multiple FIPS standards, but FIPS 140-2 is the standard that establishes four levels of security requirements for cryptographic modules. Software developers and cloud service providers often focus on becoming FIPS 140-2 compliant.
MFT Gateway
An MFT gateway establishes a highly secure access point that enables B2B data transfers while protecting your internal network. It uses reverse and forward proxies to seamlessly move data between internal and external networks. However, for security purposes, it will not store sensitive data or credentials in the DMZ.
Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation is the ability to produce proof — and establish auditability — that the intended recipient received a file. It’s also used to prove the sender's identity to the recipient. According to TechTarget, non-repudiation ensures that no party can deny that it sent or received a message.
Protocols Used to Transfer Data
Whether you’re sharing data in an email or with secure MFT software, your computer follows the rules set by a variety of universal protocols. Common protocols include:
- FTP: file transfer protocol. FTP was the first transfer protocol, and it’s still common despite its limitations. Data is not encrypted, but is password protected.
- FTPS or FTP/S: file transfer protocol secure. FTPS adds two layers of encryption (SSL/TLS) to the traditional FTP approach, which protects data in transit. It also uses certificates or passwords to authorize access to the data.
- SFTP: secure file transfer protocol. SFTP is steadily replacing FTP and FTPS protocols because it offers stronger encryption (SSH) and authentication capabilities.
- HTTP: hypertext transfer protocol. HTTP is the foundation of internet communications — it’s used by web browsers and servers to transmit data between websites and users.
- HTTPS: hypertext transfer protocol secure. HTTPS adds a layer of encryption (SSL/TLS) to HTTP communications.
Simply put, SFTP is a secure alternative to FTP and FTPS. HTTPS is a secure alternative to HTTP.
Today’s MFT platforms act as a file transfer hub. It works to consolidate governance and management of file transfers using all the above protocols. Then, it provides additional data security measures that include reverse and forward proxies for DMZ protection.
Secure File Transfer
Secure file transfer is the practice of moving data across networks while using security protocols and encryption techniques to protect the information, networks, and users that are connected to that data.
Benefits of MFT
Today’s managed file transfer solutions offer many benefits. Its wide-ranging capabilities include:
- Security and Governance: MFT eliminates the risk of insecure file exposure. There’s no need for time-consuming workarounds that may impact regulatory compliance. FIPS-compliant MFT applications can help your organization protect data. By offering a variety of file-transfer protocols, you can use the method that helps you meet compliance requirements such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOX, and GLBA. Plus, centralized MFT administration helps the team enforce organizational IT policies.
- Observability and Auditability: MFT offers end-to-end visibility of all file sharing activity, so you know the who, what, where, and when of data transfers. Quickly access file-transfer logs and analytics to audit transfer activity whenever needed — understand who is sending data, what data is being sent, where data is being sent, and when data is being sent. Additionally, you gain versioning capabilities to prevent data duplication or data loss.
- Real-Time Data Transfer: Modern managed file transfer solutions use system events to automatically trigger data transfers, in addition to time-based task scheduling. This includes transmitting, transforming, and managing files based on policy or content.
- MFT-as-a-Service: Empower employees to securely send files from email, web, and desktop applications — with zero disruption in workflow. Help your team get more done by automating data movement and enabling efficient data exchanges. Plus, eliminate the temptation to share sensitive information via unsecured methods.
- Connect to Any System: Use standard integrations or industry-standard file transfer protocols to share data across commonly used tools and applications like SAP and Informatica, as well as cloud environments like AWS, GCP, and Azure.
- Share Data Externally: Move data and files back and forth between third-party business partners, vendors, and suppliers.
- Accessibility (for All): MFT offers a single, convenient solution for everyone in the organization. Connect your file transfers to enterprise-wide data flows and workflows that span IT, operations, finance, HR, and more. Secure web-based access ensures the right data is accessible to the right people at the right time.
What Does MFT Do?
MFT puts your data on the move, transferring files between internal and external networks alike.

Internal Data Transfers
Internal data transfers allow data to flow safely and smoothly across the many internal systems of a single enterprise’s on-premises network. For this type of transmission, MFT software provides system-wide governance and observability.
External (B2B) Data Transfers
This kind of transfer allows multiple organizations to share data with external entities such as business partners, government agencies, and customers. This data is often confidential, proprietary, or personally identifiable. In other words, 100% dangerous if it lands in the wrong hands. B2B MFT solutions offer extra security measures for these external transfers, such as reverse proxies for DMZ protection.
Private and Public Cloud Data Transfers
Sometimes referred to as multi-cloud data transfers, this type of file transfer connects data that span major cloud service providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, as well as cloud storage platforms like Dropbox, SharePoint, OneDrive, and Hadoop HDFS. A solution pack, like the Inter-Cloud Data Transfer integration, enables data to stream from one object store to another without the need for intermediate storage.
Hybrid IT (On-Prem and Cloud) Data Transfers
Designed for today’s complex IT environments, these transfers move data from on-premises systems to cloud systems, and back again. Hybrid cloud file transfer solutions bridge the connectivity gap without sacrificing data integrity or security.
What’s Next in MFT: Trends and Strategies
Transfer Data to and from Containers
Containers enable faster application development, improved resource utilization, and greater portability across hybrid IT environments. No wonder they’ve become the de facto standard for application packaging and deployment for many enterprises. Here are a few videos that demonstrate a variety of strategies to transfer files to and from containers:
- Automate secure file transfers between Linux (on-prem) and an application running in an OpenShift POD
- Enable hybrid cloud file transfers using Universal Automation Center (UAC)
- Orchestrate managed file transfers with UAC, OpenShift, and Kubernetes
- How a leading insurance company uses UAC to automate file transfers with OpenShift
Transfer Data Between Private and Public Clouds
There are many reasons an enterprise may choose to keep data across multiple cloud platforms, including cost optimization, enhanced reliability, or even the desire to avoid vendor lock-in. When you need to move data across platforms and providers, see how automation saves the day:
Additional MFT Resources
For any enterprise, secure file transfers are a critical component of day-to-day operations. If it’s up to you to see them through, our experts can help lead the way.
Looking for an enterprise-grade MFT platform to securely move data from one system to another over a computer network? Stonebranch Universal Data Mover (UDM) offers maximum control, visibility, and performance. For a detailed description of UDM’s core functions and architecture, download this technical brief.
Need a secure MFT gateway for data exchanges with B2B partners? Read up on Stonebranch Universal Data Mover Gateway (UDMG), which helps you manage the flow of business-critical data between you and your external business partners, vendors, and suppliers
Interested in automating MFT across on-prem and cloud environments? When you combine UDM and UDMG with Stonebranch Universal Automation Center (UAC), you gain the ability to orchestrate file transfers in real-time — and include them in your broader business processes. UAC monitors data availability, triggers business processes when the data becomes available, and initiates data transfers from any platform in any format in a secure, reliable way. See how a hybrid cloud file transfer solution can help you seamlessly integrate your data transfers and workload automation.
Start Your Automation Initiative Now
Schedule a Live Demo with a Stonebranch Solution Expert










